Insight on the anti-poisoning mechanism of in situ coupled sulfate over iron oxide catalysts in NOx reduction†
Abstract
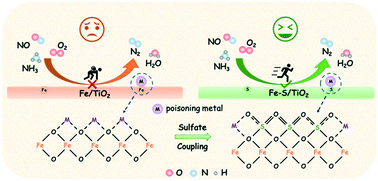
Metal poisoning is still a tough nut to crack that NOx reduction catalysts need to overcome. In this study, in situ coupled sulfate-modified iron oxide catalysts with remarkable resistance to alkali, alkaline earth, and heavy metals for NOx reduction has been demonstrated. In situ introduced sulfates were well coupled with active Fe sites to allow iron species to maintain a higher dispersion state. Moreover, in situ coupled sulfates would prefer to migrate from the bulk phase to the surface to accurately anchor metal poisons, thus protecting active sites from poisoning. High redox ability and enriched active oxygen species were both well reserved after metal poisoning, accompanied by Brønsted acidity greatly enhanced due to the presence of more sulfates on the surface. In consequence, the adsorption of NHx both on Lewis acid (–NH2) and Brønsted acid (NH4+) sites, and the formation of active adsorbed NOx species including NO−, gaseous NO2, nitro compounds were significantly accelerated. Thus, the accumulation of inert NOx species on the catalysts was greatly restrained, which promoted rapid reaction between the adsorbed NHx and NOx species, eventually contributing to high NOx reduction efficiency and metal poisoning resistance. This strategy provides a new inspiration for the poisoning-resistant reduction of NOx from stationary sources.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...