Statistical mechanics of dimerizations and its consequences for small systems†
Abstract
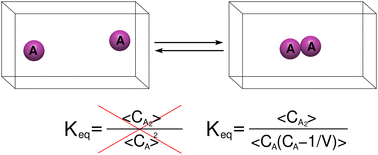
Utilizing a statistical mechanics framework, we derive the expression of the equilibrium constant for dimerization reactions. An important feature arising from the derivation is the necessity to include two-body correlations between monomer's number of particles, reminiscent to those recently found crucial for binding reactions. However in (homo-) dimerizations, particles of the same type associate, and therefore, self-correlations are excluded. As a result, the mathematical form of the equilibrium constant differs from the well-known expression given in textbooks. For systems with large number of particles the discrepancy is negligible, whereas, for finite systems it is significant. Rationalized by collision probability between monomers, the bimolecular rate for dimer formation is proportional to concentration the same way correlations are accounted for. That is average of squared, and not square of averaged, monomer concentration should be considered in such a way that inconceivable collisions between a tagged particle with itself are excluded. Another consequence emerging from these two-body correlations, is an inhomogeneous function behavior of system's properties upon scaling-down the system to a regime smaller than the thermodynamic limit. Thus, averages of properties observed at small systems are different than those observed at macroscopic systems. All predictions are verified by Monte Carlo and molecular dynamics simulations.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2022 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...