Role of hydrogen bonding in bulk aqueous phase decomposition, complexation, and covalent hydration of pyruvic acid†
Abstract
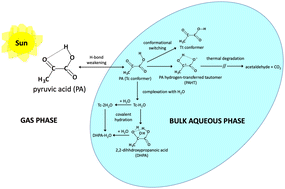
Pyruvic acid (PA) is a model for amphiphilic oxygenated organic compounds, and together with its hydrogen-bonded (H-bonded) water complexes, their presence can alter atmospheric aerosol formation. However, the fundamental understanding of PA reaction mechanisms in different environments is still being debated. Here, the role of H-bonding on PA's degradation, complexation, and covalent hydration in bulk aqueous phase is investigated theoretically. Using CCSD(T)-F12/aug-cc-pVDZ-F12 on B2PLYP-D3BJ structures with solvation model based on density, we revealed the stabilization by intramolecular H-bonding of an intermediate, PA hydrogen-transferred tautomer, altered the PA degradation mechanisms compared to gas phase. We also found that the intramolecular H-bonding in the most stable gas phase conformer (Tc) is weakened due to bulk solvation, leading to slower acetaldehyde production rate. Natural bond orbital analysis characterized the primary intermolecular H-bond in PA–water complexes as electron donation of an Owater lone pair (p) to the σ* orbital of the OH group of PA. Stronger H-bonding is correlated to p to σ* interaction, wider OH–O angles, and larger differences in the H-bond lengths between phases. The less charge difference between phases on H-bonded atoms also indicates aggressive competition of H-bonding with solvation. Water's cooperative behavior was observed by lowering the water-complexed 2,2-dihydroxypropanoic acid (DHPA–H2O) barrier from PA–water complexes compared to DHPA in both phases, stabilizing the transition state and product with intermolecular H-bonding. PA is vital in atmospheric keto-acid chemistry; thus, changes in PA reaction mechanisms in different environments due to H-bond behavior will affect aerosol formation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2022 PCCP HOT Articles

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...