Can the isonitrile biosynthesis enzyme ScoE assist with the biosynthesis of isonitrile groups in drug molecules? A computational study†
Abstract
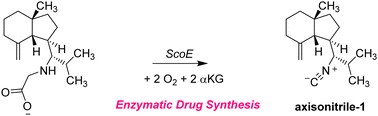
Many drug molecules contain isonitrile substituents; however, synthesizing these compounds remains challenging in organic chemistry. The isonitrile synthesizing enzyme ScoE utilizes a substrate with the γ-Gly substituent, and using two molecules of dioxygen and α-ketoglutarate converts it to an isonitrile group through an oxidative decarboxylation reaction. To explore its substrate scope and whether this process could be used for the biosynthesis of isonitrile-containing drug molecules, we performed a predictive computational study. We started with the recent crystal structure coordinates of ScoE, removed the substrate and inserted two potential precursor molecules of the drug molecules axisonitrile-1 and xanthocillin into the structure, whereby both molecules have their isonitrile groups replaced by γ-Gly. Both substrates fit into the substrate binding pocket of the enzyme well and position them in the correct orientation for catalysis on the iron center. Based on a molecular dynamics simulation, we created a quantum chemical cluster model of the enzyme active site with γ-Gly-substituted axisonitrile-1 and studied the oxidative decarboxylation reaction to form axisonitrile-1 products. The calculations give similar barriers to wildtype substrate for either the initial C–H or N–H hydrogen atom abstraction, which leads to a radical intermediate and form desaturated reactants. We then took the desaturated substrate and created another iron(IV)–oxo model complex to study the subsequent hydrogen atom abstraction and decarboxylation and found this to be feasible as well although we predict to see by-products for hydroxylation in the second cycle. Nevertheless, we believe that the ScoE enzyme can be utilized for the biosynthesis of isonitrile substituents in substrates with γ-Gly components as an environmentally benign alternative to organic chemistry approaches for the synthesis of isonitrile groups. We hope that experimental studies will be able to confirm our hypothesis.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Computational Modelling as a Tool in Catalytic Science


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...