Molecular reaction and dynamic mechanism of iodate reduction to molecular iodine by nitrogen(iii) in aqueous solution†
Abstract
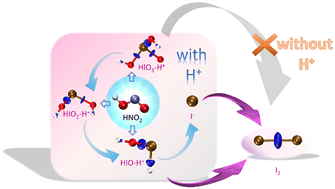
This work studies the molecular reaction and dynamic mechanism of iodate reduction by nitrogen(III) in aqueous solution using the ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) method based on density functional theory (DFT). Two possible reaction pathways (without and with H+) are proposed. The thermodynamic parameters of the proposed reaction pathways are calculated. The theoretical calculation aspects of iodate reduction, including the atomic dipole moment corrected Hirshfeld population (ADCH) atomic charge values, the intrinsic reaction coordinate (IRC) curves, the calculated interaction regional indicator (IRI) isosurfaces with the corresponding sign(λ2)ρ scatter plots, electrostatic potential (ESP) analysis and molecular reaction dynamics are discussed in-depth. The results show that the reaction pathway with H+ is confirmed based on the Gibbs free energy analysis. The transition state proved that the iodate reduction with nitrous acid undergoes four steps according to oxygen-atom deprivation. The IRC curves describe the energy change of the chemical bonds of the reactant conformations in the four steps, with an energy reduction of 71.95, 69.35, 130.15, and 125.87 kJ mol−1, respectively. The ESP interpenetration diagram and IRI isosurfaces provide detailed information on the nucleophilicity and electrophilicity of the reactant conformations. By decreasing the O atom number in HIOx (x = 1, 2, 3), the maximum positive charge decreases, and the positive charge coverage area increases, thus resulting in energy reduction and consequently a more stable conformation. Molecular reaction dynamics analytical results indicated that a relatively stable status of the reactants of the four steps was achieved after around 200 fs, and that the HIO3–HNO2 reaction released the highest energy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...