Electrochemically stimulated protein release from pH–switchable electrode–immobilized nitroavidin–biotin and avidin–iminobiotin systems†
Abstract
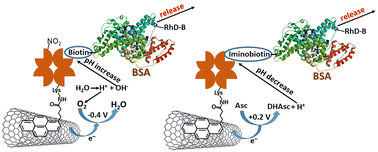
Bovine serum albumin (BSA), used as a model protein, was immobilized on a buckypaper electrode by formation of covalent bonds with avidin/iminobiotin or nitroavidin/biotin complexes. pH-sensitive affinity interactions between avidin and iminobiotin or between nitroavidin and biotin allowed splitting of the affinity bonds upon pH variation, thus resulting in BSA release. Local (interfacial) pH was changed electrochemically. The pH was decreased upon electrochemical oxidation of ascorbate or increased upon electrochemical reduction of O2. The local pH change resulted in the weakening of the affinity complexes, resulting in BSA release from the avidin/iminobiotin or nitroavidin/biotin systems when the pH was decreased or increased, respectively. Importantly, protein release was only observed when the number of chemical bonds with the affinity systems was decreased by blocking a part (ca. 50%) of the binding sites in avidin/nitroavidin with iminobiotin/biotin molecules missing the possibility of attaching the protein. Without this blocking effect, multiple bond formation with the protein preserved BSA at the electrode surface, by not allowing its release upon electrochemical pH change.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...