Quantum-coupled borophene-based heterolayers for excitonic and molecular sensing applications†
Abstract
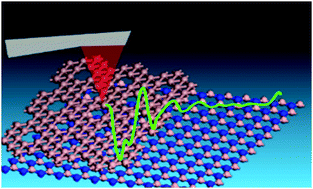
Borophene (B), with remarkably unique chemical binding in its crystallographic structural phases including anisotropic structures, theoretically has high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. Moreover, it is metallic in nature, and has recently joined the family of two-dimensional (2D) materials and is poised to be employed in flexible hetero-layered devices and sensors in fast electronic gadgets and excitonic devices. Interfacial coupling helps individual atomic sheets synergistically work in tandem, and is very crucial in controllable functionality. Most of the microscopic and spectroscopic scans reveal surface information; however, information regarding interfacial coupling is difficult to obtain. Electronic signatures of dynamic inter-layer coupling in B/boron nitride (BN) and B/molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) have been detected in the form of distinct peaks in differential current signals obtained from scanning tunneling spectroscopy (STS) and conducting atomic force microscopy (CAFM). These unique sets of observed peaks represent interfacial coupling quantum states. The peaks in the electronic density of states (DOS) obtained via density functional theory (DFT) band structure calculations matched well with the electronic signatures of coupling quantum states. In our calculations, we found that the DOS peak evolves when the component layers are brought to compromised distances. While B/BN exhibits green sensitivity indicating mid-gap formation, B/MoS2 bestows red sensitivity indicating band-gap excitation of MoS2. Molecular detection of methylene blue (MB) based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) was carried out with borophene-based hetero-layered stacks as molecular anchoring platforms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...