Temperature-dependence of the band gap in the all-inorganic perovskite CsPbI3 from room to high temperatures†
Abstract
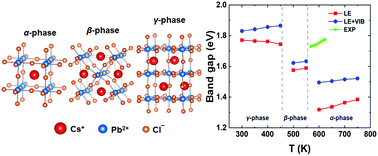
Understanding the micro-mechanism of the temperature dependence of the band gap in all-inorganic perovskites is of great significance for their optoelectronic and photovoltaic applications in various temperature environments. Herein, based on the recently developed electron-phonon renormalization method, the temperature-dependent band gaps of the optoelectronic perovskite CsPbI3 are studied from 300 K to 750 K (including orthorhombic, tetragonal, and cubic phases). It is found that the temperature-induced structural fluctuation makes the structure of perovskites deviate from the 0 K one, and the corresponding renormalized band gap differs from that at 0 K, especially for the high-temperature cubic phase (e.g., ΔEg is ∼177 meV at 600 K). However, within the temperature range of each CsPbI3 phase, the band gap Eg is enlarged slightly with the increase of temperature (e.g., ΔEg is ∼26 meV from 600 K to 750 K for the cubic phase), showing the insensitivity of the structural fluctuation effect to the temperature change. The reason is that the chemical characters of band edges are determined by PbI3−, and due to the strong correlation between Pb and I, the Pb–I bond lengths and Pb–I–Pb bond angles are almost unchanged as the temperature increases. Our work provides a fundamental understanding of the temperature-dependent band gaps in all-inorganic perovskites and shed light on the commercialization of perovskites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...