Ionic effects on supramolecular hosts: solvation and counter-ion binding in polar media†
Abstract
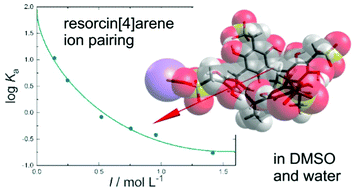
For the progress of synthetic supramolecular chemistry in aqueous solution the design of host molecules soluble in this medium is essential. A possible route is the introduction of ionic residues, with the additional advantage that also electrostatic interactions can be used to form supramolecular architectures. In this work we study the effect of different ionic substituents on a resorcin[4]arene host on solvation and counterion binding in water and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). To do so, we combine dielectric relaxation spectroscopy (DRS) at 298.15 K and dilute-solution conductivity measurements covering 278.15–308.15 K. The results indicate that studied substituents lead to a comparable increase in solubility in both water and the dipolar-aprotic DMSO. However, solvation and counterion binding not only depend on the nature of the ionic substituent but also on the solvent. Although intrinsically hydrophobic in nature, resorcin[4]arenes with ionic substituents also show strong hydrophilic hydration in water, with the extent depending on the nature of the ionic group. In contrast to that, solvophobicity apparently dominates the interactions of DMSO with the solute. Counterion binding was found for both solvents and is essentially determined by solvent polarity. It appears that, compared to neat DMSO, the solubility of the cationic resorcin[4]arene with dimethylamine substituents is strongly increased in water–DMSO mixtures due to the formation of hydrogen bonds between two DMSO molecules and one water molecule.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2022 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...