Synthesis of CxNy-rich polycyclic oligomers from primeval monomers in aqueous media†
Abstract
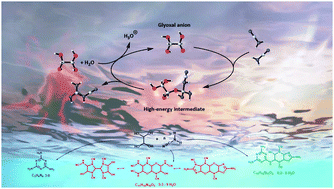
A multichannel, non-thermolytic and efficient pathway is described toward the formation of functionalized carbon nitride-like oligomers, starting from readily available cyanamide and glyoxal (in ratios >2), in aqueous media under mild conditions. Such oligomers can be isolated as stable solids that result from structures involving cyanamide self-additions along with structures formally derived from the condensation of cyanamide, dicyandiamide or melamine with glyoxal, leading occasionally to oxygen-containing units. The oligomeric aggregates have masses up to 500 u, as inferred from mass spectra analyses, and their formation can be rationalized in terms of polyadditions of cyanamide (up to 10-mer) and glyoxal. The latter is not only a willing reaction partner, but also promotes facile condensation by enhancing the reactivity of nitrile fragments and inducing a significant lowering of the energy barriers. This mechanistic surmise is also supported by DFT calculations of the early condensation steps. As a result, melamine/triazine-type structures are obtained in aquatic environments under much milder conditions than those usually required by other synthetic procedures. Moreover, our results also help unveil the abiotic processes affording complex organic matter on celestial bodies and early earth.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2022 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...