Mechanical properties of calcium silicate hydrate under uniaxial and biaxial strain conditions: a molecular dynamics study
Abstract
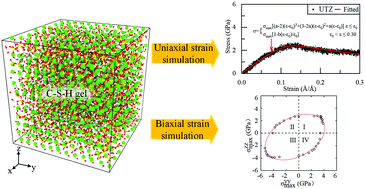
Calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) is the main hydration product of cementitious materials, often experiencing complex stress conditions in practical applications. Therefore, reactive molecular dynamics methods were used to investigate the mechanical response of the atomistic structure of C-S-H under various uniaxial and biaxial strain conditions. The results of uniaxial simulations show that C-S-H exhibits mechanical anisotropy and tension–compression asymmetry due to its layered atomistic structure. By fitting the stress–strain data, a stress–strain relationship that accurately represents the elastoplasticity of C-S-H was developed. The biaxial yield surface obtained from biaxial simulations was ellipsoidal, again reflecting the anisotropy and asymmetry of C-S-H. Four yield criteria (von Mises, Drucker–Prager, Hill, and Liu–Huang–Stout) were further investigated, and it was found that the Liu–Huang–Stout criterion can effectively capture all the major features of the yield surface. During a uniaxial tensile process in the z direction, multi-crack propagation was observed, which was aggravated and weakened by y direction tensile and compressive strains respectively. The results of chemical bond analyses revealed that, for different strain conditions, the CaW–OS and CaS–OS bonds play different roles in resisting deformation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...