Bilayer conducting salts with polymeric anions†
Abstract
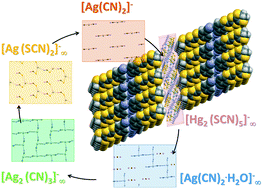
Five new salts of 5-cyanobenzene-ethylenedithio-tetrathiafulvalene (CNB-EDT-TTF), with the general formula (CNB-EDT-TTF)4A, and anions A = Ag(CN)2 (1), Ag(CN)2·H2O (2), Ag2(CN)3 (3), Ag(SCN)2 (4) and Hg2(SCN)5 (5), were prepared by electrocrystallisation and characterised by single crystal X-ray diffraction, electrical conductivity, thermoelectric power and magnetic susceptibility measurements. Their crystal structure is based on a double layer arrangement of the donors with a β′′ packing pattern identical to that previously observed in related salts with small discrete anions. The donor bilayers are separated by layers of anions which however are incoherently arranged perpendicular to the layers. The average structures obtained are compatible with anionic arrangements similar to those previously observed in single layer salts of BEDT-TTF and related donors, where, with the exception of 1, the anions are polymeric. While 2 presents electrical resistivity with a thermally activated regime, 1, 3, 4 and 5 show metallic behaviour at high temperatures, with room temperature values in the range 10–20 S cm−1 and sample dependent electronic localisation effects at lower temperatures. The thermoelectric power of these compounds is +82–90 μV K−1 at room temperature, following behavior identical to that of their analogues with small discrete anions. The paramagnetic susceptibility of 4 and 5, similar to those of their analogues with I3, PF6, AsF6 and ReO4 anions, has values of ≈1.0 × 10−3 emu mol−1 at room temperature, being significantly enhanced compared with the Pauli-type contribution predicted from electron band calculations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...