The effects of cis and trans butenedioic acid on the physicochemical behavior of lumefantrine†
Abstract
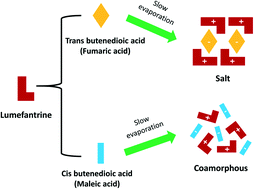
The present work investigates the effects of cis and trans butenedioic acid isomers (maleic acid and fumaric acid) on the crystallinity and pharmaceutical behavior of lumefantrine. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), attenuated total reflectance infrared spectroscopy (ATR-IR), solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (ss-NMR), and single-crystal X-ray diffraction (SC-XRD) studies were employed. Lumefantrine–fumaric acid crystallized as a salt in the monoclinic space group P21/c. In comparison, DSC and PXRD showed the formation of a co-amorphous solid with maleic acid. Complete proton transfer with a strong ionic interaction led to crystalline salt formation with the trans isomer, whereas weaker/fewer hydrogen bonds with the cis isomer of butenedioic acid led to a co-amorphous salt. The in vitro dissolution of both salts resulted in a similar 2.6–2.7-fold improvement in dissolution rate when compared to that of the crystalline lumefantrine. The crystalline and co-amorphous salts were stable under accelerated stability conditions (40 ± 2 °C and 75 ± 5% RH) for one month.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...