Development of lacto-series ganglioside fluorescent probe using late-stage sialylation and behavior analysis with single-molecule imaging†
Abstract
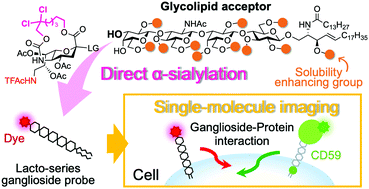
Gangliosides are a family of sialic-acid-containing glycosphingolipids that form dynamic domains (lipid rafts) with proteins in cell plasma membranes (PMs), and are involved in various biological processes. The dynamic behavior of gangliosides can be elucidated by analyzing fluorescently-labeled molecules with a powerful technique known as single-molecule imaging. We previously developed fluorescent probes for ganglioside subfamilies such as the ganglio- and globo-series, and investigated their behavior in cell PMs. This study targeted a lacto-series ganglioside, sialyl-lactotetraosylceramide, whose behavior in PMs has not yet been investigated. We applied a recently reported method for the direct sialylation of oligosaccharyl lipid acceptors to synthesize the fluorescent ganglioside probes. The glycolipid acceptor exhibited high solubility in organic solvents owing to the installation of a large quantity of p-tert-butylbenzoyl protecting groups, which ensured direct α-sialylation at relatively low temperatures. Biophysical evaluation of the synthesized probe determined that it behaved as a raft molecule in cell PMs. Furthermore, single-molecule imaging revealed cis interactions between the lacto-series ganglioside and a major raft molecule (GPI-anchored protein CD59). Moreover, the fluorescent non-sialylated (asialyl) lactotetraosylceramide behaved similarly to its sialyl counterpart.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...