Lysine methyltransferase inhibitors: where we are now
Abstract
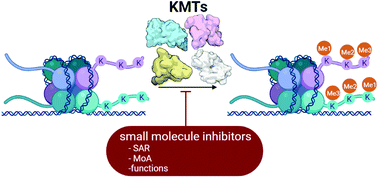
Protein lysine methyltransferases constitute a large family of epigenetic writers that catalyse the transfer of a methyl group from the cofactor S-adenosyl-L-methionine to histone- and non-histone-specific substrates. Alterations in the expression and activity of these proteins have been linked to the genesis and progress of several diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and growing defects, hence they represent interesting targets for new therapeutic approaches. Over the past two decades, the identification of modulators of lysine methyltransferases has increased tremendously, clarifying the role of these proteins in different physio-pathological states. The aim of this review is to furnish an updated outlook about the protein lysine methyltransferases disclosed modulators, reporting their potency, their mechanism of action and their eventual use in clinical and preclinical studies.
- This article is part of the themed collection: RSC Chemical Biology Transparent Peer Review Collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...