Strategy of a cell-derived extracellular matrix for the construction of an osteochondral interlayer
Abstract
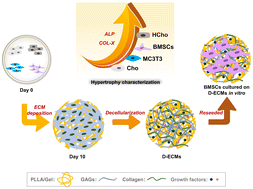
Osteochondral defects pose an enormous challenge due to the lack of an effective repair strategy. To tackle this issue, the importance of a calcified cartilage interlayer (CCL) in modulating osteochondral regeneration should be valued. Herein, we proposed that an extracellular matrix (ECM) derived from a suitable cell source might efficiently promote the formation of calcified cartilage. To the end, cell sheets from four kinds of cells, including bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), pre-osteoblasts (MC3T3), chondrocytes (Cho), and artificially induced hypertrophic chondrocytes (HCho), were obtained by seeding the cells on electrospun fibrous meshes, followed by decellularization to prepare decellularized ECMs (D-ECMs) for BMSC re-seeding and differentiation studies. For cell proliferation, the BMSC-derived D-ECM exhibited the strongest promotion effect. For inducing the hypertrophic phenotype of re-seeded BMSCs, both the BMSC-derived and HCho-derived D-ECMs demonstrated stronger capacity in up-regulating the depositions of related proteins and the expressions of marker genes, as compared to the MC3T3-derived and Cho-derived D-ECMs. Accordingly, from the histological results of their subcutaneous implantation in rats, both the BMSC-derived and HCho-derived D-ECMs displayed obvious Masson's trichrome and Safranin-O/Fast-Green staining colors simultaneously, representing the characteristics related to osteogenesis and chondrogenesis. Differently, MC3T3-derived and Cho-derived D-ECMs were mainly detected during the osteogenic or chondrogenic expression, respectively. These findings confirmed that the BMSC-derived D-ECM could induce hypertrophic chondrocytes, though being a little inferior to the HCho-derived D-ECM. Overall, the BMSC-derived D-ECM could be a potential material in constructing the interlayer for osteochondral tissue engineering scaffolds to improve the regeneration efficiency.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...