Anticancer therapeutic effect of cerium-based nanoparticles: known and unknown molecular mechanisms
Abstract
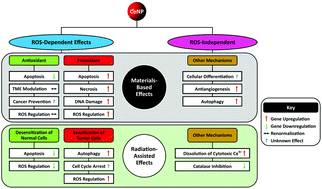
Cerium-based nanoparticles (CeNPs), particularly cerium oxide (CeO2), have been studied extensively for their antioxidant and prooxidant properties. However, their complete redox and enzyme-mimetic mechanisms of therapeutic action at the molecular level remain elusive, constraining their potential for clinical translation. Although the therapeutic effects of both antioxidant and prooxidant mechanisms generally are attributed to Ce3+ ↔ Ce4+ redox switching mediation, some studies have hinted at the involvement of unknown pathways in therapeutic effects. While redox switching is recognised increasingly as playing a key role in ROS-dependent cancer therapy, ROS-independent cytotoxicity mechanisms, such as Ce4+ dissolution and autophagy, also are emerging as being of importance. Although ROS-mediated prooxidant therapies are the most intensively studied, particularly in the context of cancer, the antioxidant activity deriving from the redox switching, particularly during radiation therapy, also plays an important role in the protection of normal cells during radiation therapy, hence reducing adverse effects. Since cancer cell proliferation results in aberrant behaviour of the tumour microenvironment (TME), then CeNP-based therapies are being used to address a multiplicity of known and unknown factors that aim to normalise the TME and thus prevent this aberrant behaviour. Although it is perceived that the pH plays a key role in the therapeutic performance of cerium-based nanoparticles, this is not conclusive because the relative importances of other factors, particularly Ce dissolution, Ce3+/Ce4+ ratio, cellular H2O2 level, and the role of anions, remain poorly understood. Consequently, the present work explores these multiple chemistry-driven mechanisms, which are both ROS-dependent and ROS-independent, in cancer therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...