Enhancement of intercellular interaction between iPSC-derived neural progenitor cells and activated endothelial cells using cell surface modification with functional oligopeptides†
Abstract
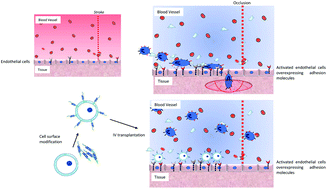
Cell-based therapy has been used to treat stroke related disorders, which have no treatment options available 4.5 hours after onset. Although the administration of tissue plasminogen activator and mechanical thrombectomy are potent treatments, their clinical implementation is limited within the available time. Here, we aimed to use induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural progenitor cells (NPCs) for stroke treatment with higher delivery efficiency in stroke areas, which will improve the therapeutic effect. E-selectin binding oligopeptide (Esbp) was conjugated with poly(ethylene glycol)-conjugated-lipid (Esbp-PEG-lipid) with different molecular weights of PEG (5 and 40 kDa) for cell surface modification. Then, we optimized the cell surface modification of NPCs by studying cell-binding ability onto the model surfaces of stroke areas, such as recombinant E-selectin-immobilized surfaces and TNF-α activated endothelium. As a result, the cell surface modification of NPCs with Esbp-PEG-lipid was found to induce specific intercellular interactions with the activated endothelium through the binding of Esbp with E-selectin. Additionally, the shorter PEG spacer was suitable for intercellular interactions. Thus, our technique shows potential for use in cell therapy with enhanced cell accumulation in infarct areas.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...