Recent development in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography stationary materials for glycopeptide analysis
Abstract
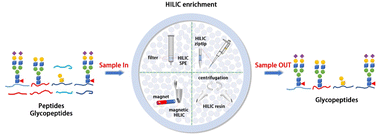
Protein glycosylation is one of the most important post-translational modifications, and aberrant glycosylation is associated with the occurrence and development of diseases. Deciphering abnormal glycosylation changes can identify disease-specific signatures to facilitate the discovery of potential disease biomarkers. However, glycosylation analysis is challenging due to the diversity of glycans, heterogeneity of glycosites, and poor electrospray ionization of mass spectrometry. To overcome these obstacles, glycosylation is often elucidated using enriched glycopeptides by removing highly abundant non-glycopeptides. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) is widely used for glycopeptide enrichment due to its excellent selectivity and specificity to hydrophilic glycans and compatibility with mass spectrometry. However, the development of HILIC has lagged far behind hydrophobic interaction chromatography, so efforts to further improve the performance of HILIC are beneficial for glycosylation analysis. This review discusses recent developments in HILIC materials and their advanced applications. Based on the physiochemical properties of glycopeptides, the use of amino acids or peptides as stationary phases showed improved enrichment and separation of glycopeptides. We can envision that the use of glycopeptides as stationary phases would definitely further improve the selectivity and specificity of HILIC for glycosylation analysis.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analytical Methods Review Articles 2022


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...