A simple and cost-effective smartphone-based digital imaging device for the quantification of selected heavy metals in Thai rice†
Abstract
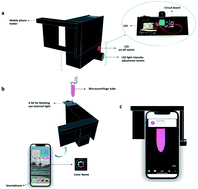
This paper describes smartphone-based digital imaging equipment for lead, cadmium, copper, and zinc determination in Thai rice that is both convenient and cost-effective. This smartphone-based digital imaging device has a built-in light control box made of poly(lactic acid) or PLA, a compostable and biodegradable plastic, with a light control circuit box underneath that uses a single white light-emitting diode (LED) lamp and takes photos at only 20 lux, which is very low but clearly captures the color of heavy metal complexes. In the present study, the dithizone ligand in different buffers is employed to produce a specific color solution for each heavy metal. According to the output from the free Color Name application, the concentration of heavy metals is proportional to the intensity of the resulting red color. A linear range of 0.1–1.0 mg L−1 was obtained. The lower detection limit was determined to be between 0.01 and 0.05 mg L−1, whereas the quantification limit was in the range from 0.04 to 0.15 mg L−1. The intra-day precision (%RSD, n = 5) was 0.4–0.8 with high consistency, while the inter-day precision (%RSD, n = 5) was 0.5–0.8 with good efficacy. The recovery rate for heavy metals added to samples of Thai rice ranged from 99.4 to 105.5 percent. Heavy metals were detected in a variety of rice samples utilizing the smartphone-based digital imaging equipment, with acceptable accuracy when compared to atomic absorption spectrophotometric data using a paired t-test. This smartphone-based digital imaging is efficient, accessible, and cost-effective, and it provides a viable alternative to existing heavy metal detection methods in Thai rice.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...