In situ interferometry study of ionic mass transfer phenomenon during the electrodeposition and dissolution of Li metal in solvate ionic liquids†
Abstract
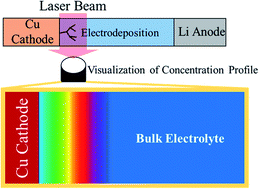
A digital holographic microscope was used to observe the Li+ concentration profile in situ, accompanied by the electrodeposition and electrochemical dissolution of Li metal in a solvate ionic liquid. The concentration profile showed a linear relationship with the square root of time in a quasi-two-dimensional electrochemical cell that could restrict natural convection fluid motion. For the anodic reaction, the electrochemical dissolution of Li metal induced an increase in concentration in the vicinity of the anode surface. Solvate ionic liquids have an enormous Li salt concentration, and the concentration increase induces a drastic increase in the viscosity of the electrolyte, resulting in a change in cell voltage. In situ Raman spectroscopy supported the development of the concentration profile near the electrode surface. The coordination of the chemical species also changed with the development of concentration profile induced by electrodeposition and electrochemical dissolution of Li metal in the solvate ionic liquid. This study emphasizes that the development of a concentration profile is more important for a concentrated electrolyte (e.g., solvated ionic liquid) than a conventional 1 M class battery electrolyte. This is because the concentration in the vicinity of the electrode can deviate from the ideal molar ratio of Li salt and solvents due to the electrochemical reaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...