Development of ultraviolet-B long-lived persistent phosphors in Pr3+-doped garnets†
Abstract
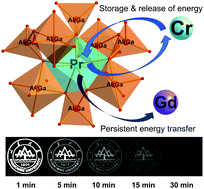
Inorganic luminescent materials that emit in the ultraviolet-B (UVB) region (280–320 nm) have gained considerable attention in recent years because of the growing demands for applications in photochemistry and photomedicine. However, most of the available UVB phosphors are photoluminescent, for which continuous external excitation is essential. This common but very inconvenient luminescence form hinders the further development of UVB luminescence technology. Here, we report the design and development of a series of Pr3+-doped garnet-based UVB persistent phosphors by combining conduction band engineering, the vacuum referred binding energy (VRBE) diagram and persistent energy transfer control. The developed UVB persistent phosphors can not only be charged using a standard 254 nm UV lamp but also natural sunlight, leading to an intense and long-lasting UVB afterglow of more than 60 h. Besides, the persistent luminescence properties and trap charging and detrapping processes are comprehensively investigated using persistent luminescence excitation spectra and thermoluminescence experiments to uncover the possible luminescence mechanism in these phosphors. More importantly, the unique UVB persistent light emission from these garnet phosphors can be clearly imaged and recorded using a UVB camera in a bright indoor-lighting environment because of the zero-background noise from indoor ambient light, indicating that these UVB persistent phosphors have important application potential for optical tagging and optical data storage in a bright environment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...