Lenvatinib and Cu2−xS nanocrystals co-encapsulated in poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy against advanced hepatocellular carcinoma†
Abstract
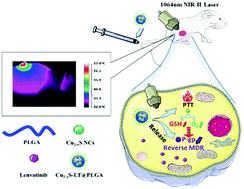
Lenvatinib (LT) is gradually replacing sorafenib as an alternative targeted drug against advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the anticancer effects of LT are still limited because of its low cytotoxicity, multidrug resistance (MDR), and tumor relapse. Herein, we constructed a smart biophotonic nanoplatform to overcome the barriers preventing high performance. LT and copper sulfide nanocrystals (Cu2−xS NCs) with excellent photothermal properties in the near-infrared-II (NIR-II) zone were co-encapsulated in poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) through nanoprecipitation. Both in vitro and in vivo evaluations demonstrated that Cu2−xS NCs enhanced the anticancer efficacy of LT, without recurrence. In addition, the presence of copper ions could allow glutathione (GHS) to be consumed and oxygen to be produced, likely suppressing the expression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and overcoming the issue of MDR relating to LT. More importantly, synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy with LT and Cu2−xS NCs was more effective than any single therapy or theoretical combination. This nanoplatform is promising for advancing future LT-based treatment strategies for HCC therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...