Bioadhesive glycosylated nanoformulations for extended trans-corneal drug delivery to suppress corneal neovascularization†
Abstract
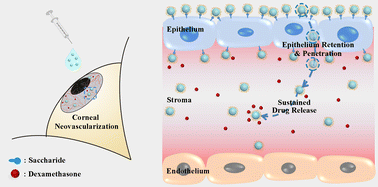
Eye-drop formulations as conventional regimens to tackle ocular diseases are far from efficient due to the rapid clearance by eye tears and the blockage of the corneal epithelium barrier. Here, we describe a bioadhesive glycosylated nanoplatform with boric acid pendants as a drug carrier for noninvasive trans-corneal delivery of drugs to treat corneal neovascularization (CNV), a serious corneal disease resulting in significant vision impairment. This biocompatible nanoplatform is formulated from a synthetic amphiphilic boric acid-based copolymer self-assembling to form highly stable micelles with a high loading capacity for dexamethasone (DEX). The nanoplatform is demonstrated to be in contact with the corneal epithelium for a long period under the bioadhesive function of boric acid modules and releases the drug over 96 h in a controlled manner. Our results also suggest that the nanoplatform can be efficiently internalized by corneal epithelial cells in vitro and realize transcytosis in vivo to greatly enhance the transcorneal penetration of the loaded drugs into the pathological corneal stroma. On topical application against rat corneal alkali burn, the nanoformulation presents more robust efficacy on neovascularization suppression and inflammation elimination than free DEX with a negligible effect on normal tissues. This bioadhesive strategy which focuses on extending ocular drug retention and improving trans-corneal drug delivery not only highlights an approach for alternative noninvasive therapy of CNV but also provides a versatile paradigm for other biomedical applications by overcoming protective barriers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...