Rapid build-up of high-throughput screening microarrays with biochemistry gradients via light-induced thiol–ene “click” chemistry†
Abstract
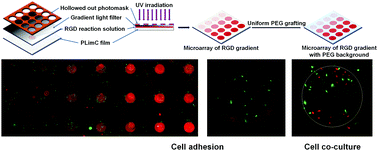
Microarrays have become extremely powerful experimental tools for high-throughput screening of cell behaviors in multivariate microenvironments. Herein, a microarray-based high-throughput platform with biochemistry gradients was developed using poly(limonene carbonate) (PLimC) as a substrate through thiol–ene click chemistry. ATR-IR, XPS, Raman spectrum, and water contact angle results demonstrated that the sulfhydryl molecules, including PEG (polyethylene glycol) and RGD (arginine-glycine-aspartic acid) peptide, could be grafted onto PLimC substrates, while the grafting density could be well controlled by regulating the intensity of UV irradiation. Then, microarrays with a gradient of RGD grafting density were fabricated by using UV irradiation patterned by a photomask and a gradient light filter. Adhesion experiments of smooth muscle cells and 3T3-L1 mouse embryonic fibroblast cells proved that the cell behaviors were highly determined by the RGD density. This platform puts forward a facile, high-throughput method to study the effect of biochemical signal density on cell behaviors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...