Intermolecular B–N coordination and multi-interaction synergism induced selective glycoprotein adsorption by phenylboronic acid-functionalized magnetic composites under acidic and neutral conditions†
Abstract
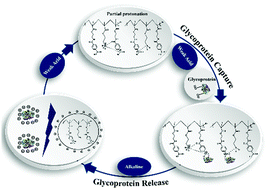
Abnormal protein glycosylation is associated with many diseases including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. Therefore, selective capturing of glycoproteins under physiological or weak acid conditions (tumor microenvironment) is vital for disease diagnosis and further comprehensive analysis. Here, we propose a strategy of intermolecular B–N bond-based phenylboronic acid affinity to capture glycoproteins under neutral and slightly acidic conditions. Surprisingly, the captured glycoproteins were released in alkaline solution. This is contrary to the traditional phenylboric acid affinity, and we studied this from the perspective of materials, proteins, and incubation conditions. We identified the synergistic effect of intermolecular B–N bond-based phenylboronic acid affinity, electrostatic interaction, and polymer brush structure-based glycoprotein adsorption under slightly acidic conditions. The electrostatic repulsion between Fe3O4@SiO2@poly (2-aminoethyl methacrylate hydrochloride)-4-carboxyphenylboronic acid (Fe3O4@SiO2@PAMA-CPBA) nanoparticles and transferrin (TRF) was far greater than the specific binding between phenylboric acid of CPBA and glycosylation residues of TRF resulting in the release of the captured glycoproteins in alkaline solution. Fe3O4@SiO2@PAMA-CPBA nanoparticles exhibited different selectivity capabilities toward different glycoproteins in multiprotein solutions due to protein interactions. These results may pave a new way for the design of phenylboric acid-based materials towards glycoprotein adsorption in a physiological environment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...