Anisotropic anion exchange membranes with extremely high water uptake for water electrolysis and fuel cells†
Abstract
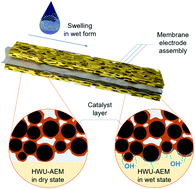
The poor interfacial contact between an ion-conducting membrane and electrodes and the resulting sluggish mass transport have been long recognized as the hurdles for the further development of electrochemical conversion devices, especially for hydrogen energy conversion technologies such as anion exchange membrane fuel cell (AEMFC) and anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE) technologies. Thus, mass transfer intensification at the interface between a membrane and catalyst (solid–solid interface) is one of the most essential requirements for boosting the performance of the aforementioned technologies. Here we fabricated an extremely high water uptake anion exchange membrane (HWU-AEM) with a huge swelling behavior in the through-plane direction (485.3% of original thickness), whereas that in the in-plane direction shows negligible swelling (7.8%). The anisotropic swelling behavior not only facilitates the AEM to adaptively fill the micro-gaps between the membrane and catalyst layer thereby greatly alleviating the sluggish interfacial mass transfer, but also simultaneously enables a dimensional stability of the prepared AEM. In addition, the extremely high water uptake of AEM enables an efficient water-management at the catalyst surface. Due to this design, besides an outstanding hydroxide conductivity and chemical and mechanical stability, an excellent performance of 0.911 A cm−2 at 1.9 V of AEMWE at room temperature shows preponderance in hydrogen production applications. Meanwhile, a preeminent peak power density of 1.1 W cm−2 at 80 °C is achieved when assembled in a H2/O2 fuel cell with a HWU-AEM. The HWU-AEM may provide new design principles for fuel cell, water electrolysis and other electrochemical devices, which generally suffer from sluggish heterogeneous interfacial mass transport.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...