Applications of thermodynamic calculations to practical TEG design: Mg2(Si0.3Sn0.7)/Cu interconnections†
Abstract
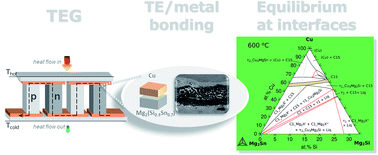
Magnesium silicide stannide solid solutions, Mg2(Si,Sn), are prominent materials in the development of devices for thermoelectric energy conversion for intermediate operating temperatures, owing to the high values of their thermoelectric figure of merit zT, elemental abundance, and non-toxicity. The manufacturing of thermoelectric generators, however, relies also upon long-term stable contacts with low thermal and electrical resistivity and good bonding of the metallic contact bridge (electrode) to the thermoelectric legs of Mg2(Si,Sn) with a similar thermal expansion coefficient. In the assembly of thermoelectric generators, the thermoelectric legs have to be bonded to metallic electrodes to establish an electrical circuit. In this work, contacts between Mg2(Si0.3Sn0.7) and Cu were made at 600 °C and investigated using thermodynamic equilibrium calculations to gain understanding on the phase transformations occurring in the bonding process. Cu is selected as a metallic electrode as it is a highly conductive element with a thermal expansion coefficient similar to that of the thermoelectric material. Contacting methods usually deviate from equilibrium conditions; nevertheless, we use this contact couple to illustrate that equilibrium thermodynamic considerations are an efficient support to anticipate and identify the reaction products forming the final microstructure of the bonded region, and ultimately, for improving the contact design. A thermodynamic database of Gibbs energies for quaternary Cu–Mg–Si–Sn was built up and made available in this work. With this database, thermodynamic calculations were done in order to complement the experimental observations on the microstructure and thermochemistry of the Mg2(Si0.3Sn0.7)/Cu interconnections. The approach developed in this work is general and therefore applicable to the investigations of different thermoelectric materials and/or metallic electrodes, by enlarging the thermodynamic description, providing an effective guide to the experimental settings of the contacting process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...