Synthesis of graphene mesosponge via catalytic methane decomposition on magnesium oxide†
Abstract
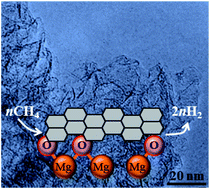
Graphene mesosponge (GMS) is a new class of mesoporous carbon consisting mainly of single-layer graphene walls. GMS has traditionally been synthesized via chemical vapour deposition (CVD) of methane onto a template of alumina (Al2O3) nanoparticles, which catalyses methane conversion. However, the Al2O3 template needs to be removed using costly and environmentally concerning processes such as hydrofluoric acid or concentrated base. In this work, we examine methane conversion catalysed by magnesium oxide (MgO) and utilized MgO as an alternative catalytic template. In contrast to Al2O3, a solid acid catalyst, MgO is a solid base catalyst that is also active for methane conversion into graphene sheets but dissolves easily in hydrochloric acid. We have investigated the reaction mechanism using in situ weight measurements and gas-emission analysis during CVD complemented by density functional theory calculations. We found that the pure MgO surface is activated via O-elimination with methane above 778 °C. On the activated MgO surface, methane is converted into a graphene sheet with a relatively low activation energy of 134 kJ mol−1. Once the first graphene layer is formed, the methane-to-graphene conversion rate decreases and the activation energy increases to 234 kJ mol−1, which is comparable to that reported in thermal methane-CVD on carbon. As a result of the faster growth rate of the first layer with respect to additional layers, it is easier to obtain single-graphene layers using MgO. The MgO-derived GMS has a unique combination of properties including a high surface area, developed mesopores, high oxidation resistance, significant softness and elasticity, very low bulk modulus (0.05 GPa), and force-driven reversible liquid–gas phase transition. Thus, we expect the MgO-derived GMS can be employed in a variety of applications including high-voltage supercapacitors and as a new type of heat pump based on the force-driven phase transition.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...