Three-dimensional construction of electrode materials using TiC nanoarray substrates for highly efficient electrogeneration of sulfate radicals and molecular hydrogen in a single electrolysis cell†
Abstract
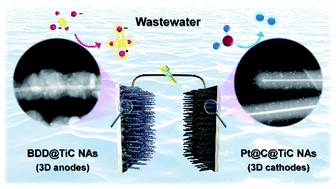
The development of three-dimensional electrode substrates is a strategy for designing powerful electrolysis cells for hydrogen production combined with electrochemical oxidation of various refractory organic compounds. Herein, to achieve highly effective and low-cost anodic treatment of pollutants and simultaneous cathodic hydrogen evolution in a single electrolysis cell containing sulfate-laden wastewater, we fabricated carbon-coated TiC nanoarrays (C@TiC NAs) as efficient three-dimensional (3D) electroactive supports. The anodes prepared via the deposition of boron-doped diamond (BDD) on 3D C@TiC NAs (BDD@TiC NAs) exhibited 1.9-fold higher efficiency for benzoic acid degradation and 4.4-fold higher peroxydisulfate (PDS) generation than the conventional plate type BDD electrode. Moreover, with multi-activity assessment using 8 organic substances, the BDD@TiC NAs enabled successful anodic treatment of all tested refractory organics and the kinetic rate did not depend on the substrate type. For the cathode, Pt nano-dots (NDs) coated on C@TiC NAs (Pt@C@TiC NAs) can be simply prepared via salt coating and subsequent thermal reduction. Uniformly decorated Pt NDs with a low mass loading of 0.029 mg cm−2 on C@TiC NAs showed the same hydrogen evolution reaction performance as that of a commercial Pt plate. When a single electrolysis cell was configured using BDD@TiC NAs and Pt@C@TiC NAs, the cell performance surpassed that of a conventional ideal electrolysis cell (flat BDD//Pt plate) in all efficiency aspects: degradation of benzoic acid, sulfate radical generation, and hydrogen production.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...