Triggering photocatalytic activity of carbon dot-based nanocomposites by a self-supplying peroxide†
Abstract
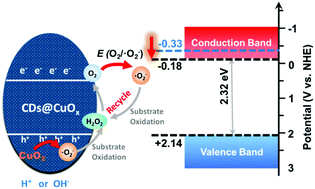
The performance of photocatalysts highly relies on the carrier quantity transferred from the bulk to the surface during the catalytic process. However, the polarization electric field induced by charge accumulation at the surface easily causes recombination, and thus leads to the decrease of the charge quantity involved in the chemical reaction. Here we presented a carbon dot-based composite (CDs@CuOx) and discovered that it can eliminate the charge accumulation by means of chemical reaction triggered by the self-supplying peroxide. Moreover, the in situ generated O2 and the enlarged band gap induced by carbon dots synergistically reduced the reaction barrier from O2 to a superoxide radical (˙O2−), and thus helped to form the rapid chemical reaction loop of ˙O2−, H2O2 and O2. This rapid chemical conversion promptly consumed photoinduced electrons and holes to eliminate the surface polarization and remarkably boosted the photocatalytic activity of CDs@CuOx by attaining a 35 times higher maximum reaction rate than CuOx.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...