Ni-based bimetallic nano-catalysts anchored on BaZr0.4Ce0.4Y0.1Yb0.1O3−δ for internal steam reforming of methane in a low-temperature proton-conducting ceramic fuel cell†
Abstract
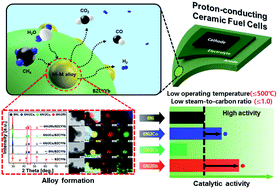
This study reports the catalytic performance of 8Ni (8 wt% Ni) and 6Ni2M (6 wt% Ni, 2 wt% M (M: Co, Cu, Rh)) anchored on BaZr0.4Ce0.4Y0.1Yb0.1O3−δ, an anode backbone material of proton-conducting ceramic fuel cells (PCFCs), for steam reforming of methane at low temperatures (350–550 °C). Results show that all catalysts have coherent structural properties and form bimetallic alloys. Their catalytic activities are evaluated at various temperatures, steam-to-carbon ratios, and gas flow rates. It is shown that 6Ni2Rh has the highest catalytic activity under all operating conditions. 6Ni2Rh and 6Ni2Co exhibit higher methane conversion and hydrogen yield than 8Ni even at low steam-to-carbon ratios. Their high activities make them less dependent on gas flow rate. They show higher resistance to carbon formation and maintain their catalytic activities during long-term operation. 6Ni2Rh and 6Ni2Co can respond to diverse operating conditions of direct methane-fueled PCFCs while maintaining high catalytic activity and stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...