Recent progresses in the mechanism, performance, and fabrication methods of metal-derived nanomaterials for efficient electrochemical CO2 reduction
Abstract
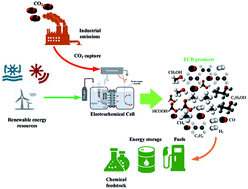
The electrochemical CO2 reduction (ECR) to produce valuable chemicals and fuels using clean energy resources is a promising and effective route to support energy storage and reduce the large CO2 concentration to avoid climate change. Among the presently adopted CO2 conversion technologies, electrochemical CO2 reduction (ECR) to valuable feedstock is presently a concern of critical research effort as a technology that can concurrently enable CO2 reduction and the storage of renewable energy. The ECR performance and economic viability are greatly influenced by the intrinsic characteristics of the catalyst employed. Many techniques have been practiced to improve the catalytic performance of heterogeneous catalysts by administering their morphology, size, crystal facets, grain boundaries, and surface defects and their integration with other synergistic constituents to fabricate nanomaterials. Presently, the fabrication of nanomaterials at the atomic level is an effective and strong technique to address the particular issues of catalytic performance and durability in ECR, by comprehending the structure–performance relationship of the nanomaterials. Herein, we present the recent technological advances with metal-derived nanomaterials, discussing the factors affecting their catalytic performance, their mechanism, and applications for the selective production of formic acid, carbon monoxide, alcohols, and hydrocarbons. Moreover, different commonly-adopted fabrication techniques for the synthesis of nanostructures have been incorporated to outline their working principles and their specialty to produce different kinds of nanostructures (nano-polyhedrons, nanowires, dendrites, and nano-frames).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...