A reductive ion exchange strategy using NaTi2(PO4)3 for metal removal/recovery from wastewater†
Abstract
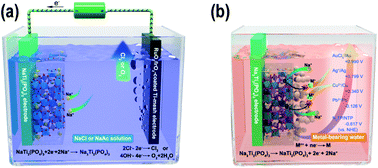
With the increasing concerns about energy and environments, there are growing demands for efficient metal removal/recovery strategies for environmental protection and sustainable development. Here, a novel reductive ion exchange (RIE) strategy is proposed to use faradaic electrode materials, such as NaTi2(PO4)3 (NTP), for metal removal/recovery from wastewater. For a pre-charged Na3Ti2(PO4)3 in metal-bearing water, the potential differences between the NTP film and the reducible metal ions (such as Pb, Cu, Ag and Au) drive a rapid metal reduction process, which produces metallic nanoparticles, while the NTP film is discharged by the release of Na ions. Compared to the common adsorption-based methods, the NTP film provides a large electrical force to capture and reduce the specific metal ions, which highly increases its efficiency in removing trace amounts of metal ions from water. We show that by using an as-assembled NTP-based device the reducible metal concentrations all drop by two orders of magnitude at both the ppm and ppb levels. More interestingly, the reduced nanoparticles are loosely attached on the surface of the NTP films and can be facilely separated and recycled, converting metal pollutants into valuable materials without utilizing reductive agents or high temperature thermal treatments. Also, the charging of NTP is in Na-bearing water instead of wastewater; therefore, the film contamination by the organic matter and other unreducible cations in wastewater can be avoided, and the NTP film can be recharged and reused for hundreds of times. Our research brings a new strategy for recycling trace amounts of valuable noble metal ions from wastewater. It may also bring new insights in the application of the traditional faradaic electrode materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...