Hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels loaded with chemoattractant and anticancer drug – new formulation for attracting and tackling glioma cells†
Abstract
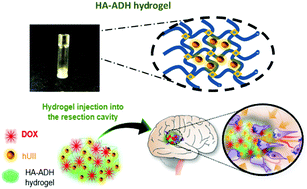
Over the last few years, significant interest has emerged in the development of localised therapeutic strategies for the treatment of glioblastoma (GBM). The concept of attracting and trapping residual tumour cells within a confined area to facilitate their eradication has developed progressively. Herein, we propose a new design of hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel which can be utilized as a matrix containing a soluble chemoattractant to attract residual glioma cells and chemotherapeutic agents to eradicate them in a less invasive and more efficient way compared to the currently available methods. Hydrogels were prepared at different crosslinking densities, e.g. low and high density, by crosslinking hyaluronic acid with various concentrations of adipic acid dihydrazide and U87MG GBM cell morphology, survival and CD44 expression were evaluated. As a proof-of-concept, hydrogels were loaded with a small peptide chemokine, human urotensin II (hUII), and the migration and survival of U87MG GBM cells were studied. Chemoattractant-containing hydrogels were also loaded with chemotherapeutic drugs to promote cell death in culture. The results showed that U87MG cells were able to invade the hydrogel network and to migrate in response to the chemoattractant hUII. In addition, in static condition, hydrogels loaded with doxorubicin demonstrated significant cytotoxicity leading to less than 80% U87MG cell viability after 48 hours when compared to the control sample. In addition, in in vitro invasive assays, it was originally shown that the chemoattractant effect of hUII can be effective before the cytotoxic action of doxorubicin on the U87MG cells trapped in the hydrogel. Our results provide new insights into a promising approach which can be readily translated in vivo for the treatment of one of the most devastating brain tumours.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Soft matter aspects of cancer


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...