Measuring colloid–surface interaction forces in parallel using fluorescence centrifuge force microscopy†
Abstract
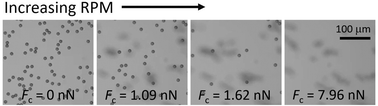
Interactions between colloidal-scale structures govern the physical properties of soft and biological materials, and knowledge of the forces associated with these interactions is critical for understanding and controlling these materials. A common approach to quantify colloidal interactions is to measure the interaction forces between colloids and a fixed surface. The centrifuge force microscope (CFM), a miniaturized microscope inside a centrifuge, is capable of performing hundreds of force measurements in parallel over a wide force range (10−2 to 104 pN), but CFM instruments are not widely used to measure colloid–surface interaction forces. In addition, current CFM instruments rely on brightfield illumination and are not capable of fluorescence microscopy. Here we present a fluorescence CFM (F-CFM) that combines both fluorescence and brightfield microscopy and demonstrate its use for measuring microscale colloidal-surface interaction forces. The F-CFM operates at speeds up to 5000 RPM, 2.5× faster than those previously reported, yielding a 6.25× greater maximum force than previous instruments. A battery-powered GoPro video camera enables real-time viewing of the microscopy video on a mobile device, and frequency analysis of the audio signal correlates centrifuge rotational speed with the video signal. To demonstrate the capability of the F-CFM, we measure the force required to detach hundreds of electrostatically stabilized colloidal microspheres attached to a charged glass surface as a function of ionic strength and compare the resulting force distributions with an approximated DLVO theory. The F-CFM will enable microscale force measurements to be correlated with fluorescence imaging in soft and biological systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...