Channel-length dependence of particle diffusivity in confinement†
Abstract
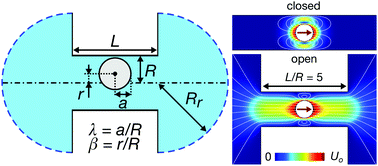
Understanding the diffusive behavior of particles and large molecules in channels is of fundamental importance in biological and synthetic systems, such as channel proteins, nanopores, and nanofluidics. Although theoretical and numerical modelings have suggested some solutions, these models have not been fully supported with direct experimental measurements. Here, we demonstrate that experimental diffusion coefficients of particles in finite open-ended channels are always higher than the prediction based on the conventional theoretical model of infinitely long channels. By combining microfluidic experiments, numerical simulations, and analytical modeling, we show that diffusion coefficients are dependent not only on the radius ratio but also on the channel length, the boundary conditions of the neighboring reservoirs, and the compressibility of the medium.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...