Quantitative analysis of bending hysteresis by real-time monitoring of curvature in flexible polymeric films†
Abstract
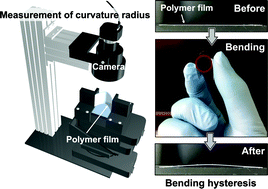
Flexibility, viscoelasticity and stress–strain relation in bending polymeric films are key factors in designing mechanically durable flexible electronic devices and soft robots. However, bending hysteresis, which appears as a precursor phenomenon of fracture and fatigue, remains unclear; no one quantitatively evaluated a bending curvature causing hysteresis. Herein, we report the bending hysteresis of polymeric films used as common substrates in flexible electronics by precisely monitoring bending curvatures. By real-time measuring curvatures of films upon bending and subsequent unbending, we have successfully determined the curvatures that cause the hysteresis. These curvatures also depend on a film thickness. Furthermore, we revealed that the occurrence of bending hysteresis is explained by bending strains that have a nonlinear relation with internal stresses. This enables us to predict strain limits that cause the bending hysteresis, based on a stress–strain curve of polymeric films.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...