Nano-pump based on exothermic surface reactions†
Abstract
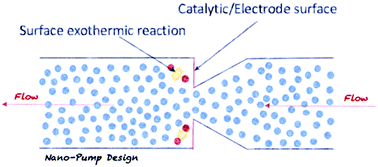
We present simulations indicating that it should be possible to construct a switchable nano-scale fluid pump, driven by exothermic surface reactions. Such a pump could, for instance, be controlled electro-chemically. In our simulations we explore a simple illustration of such a pump. We argue that the simplicity of the pump design could make it attractive for micro/nano-fluidics applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...