Protein–nanoparticle interactions and a new insight
Abstract
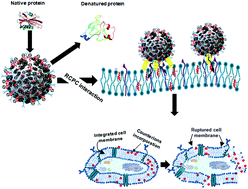
The study of protein–nanoparticle interactions provides knowledge about the bio-reactivity of nanoparticles, and creates a database of nanoparticles for applications in nanomedicine, nanodiagnosis, and nanotherapy. The problem arises when nanoparticles come in contact with physiological fluids such as plasma or serum, wherein they interact with the proteins (or other biomolecules). This interaction leads to the coating of proteins on the nanoparticle surface, mostly due to the electrostatic interaction, called ‘corona’. These proteins are usually partially unfolded. The protein corona can deter nanoparticles from their targeted functionalities, such as drug/DNA delivery at the site and fluorescence tagging of diseased tissues. The protein corona also has many repercussions on cellular intake, inflammation, accumulation, degradation, and clearance of the nanoparticles from the body depending on the exposed part of the proteins. Hence, the protein–nanoparticle interaction and the configuration of the bound-proteins on the nanosurface need thorough investigation and understanding. Several techniques such as DLS and zeta potential measurement, UV-vis spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, circular dichroism, FTIR, and DSC provide valuable information in the protein–nanoparticle interaction study. Besides, theoretical simulations also provide additional understanding. Despite a lot of research publications, the fundamental question remained unresolved. Can we aim for the application of functional nanoparticles in medicine? A new insight, given by us, in this article assumes a reasonable solution to this crucial question.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...