Critical Casimir interactions of colloids in micellar critical solutions
Abstract
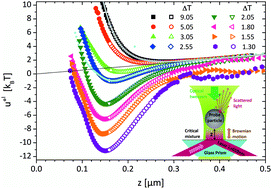
We study the temperature-dependence of critical Casimir interactions in a critical micellar solution of the nonionic surfactant C12E5 dissolved in water. Experimentally, this is achieved with total internal reflection microscopy (TIRM) which measures the interaction between a single particle and a flat wall. For comparison, we also studied the pair interactions of a two dimensional layer of colloidal particles in the identical micellar system which yields good agreement with the TIRM results. Although, at the surfactant concentration considered here, the fluid forms a dynamical network of wormlike micelles whose structure is considerably more complex than that of simple critical molecular fluids, the temperature-dependence of the measured interactions is – for surface-to-surface distances above 160 nm – in excellent quantitative agreement with theory. Below 160 nm, deviations arise which we attribute to the adsorption of micelles to the interacting surfaces.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...