Exploring secondary interactions and the role of temperature in moisture-contaminated polymer networks through molecular simulations†
Abstract
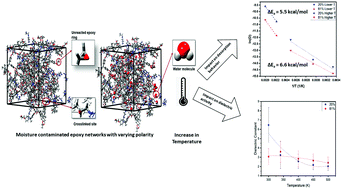
Leveraging the state of absorbed moisture within a polymer network to identify physical and chemical features of the host material is predicated upon a clear understanding of the interaction between the polymer and a penetrant water molecule; an understanding that has remained elusive. Recent work has revealed that a novel damage detection method that exploits the very low baseline levels of water typically found in polymer matrix composites (PMC) may be a valuable tool in the composite NDE arsenal, provided that a clear understanding of polymer–water interaction can be obtained. Precise detection, location, and possible quantification of the extent of damage can be performed by characterizing the physical and chemical states of moisture present in an in-service PMC. Composite structures have a locally elevated dielectric constant near the damage sites due to a higher fraction of bulk (“free”) water, which has a higher dielectric constant when compared to water molecules bound to the polymer network through secondary bonding interactions. In this study, we aim to get a clear atomistic scale picture of the interactions which drive the dielectric signature variations necessary for tracking damage. Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations were used to explore the effect of temperature on the state of moisture in two epoxy matrices with identical chemical constituents but different morphologies. The motivation was to understand whether higher polarity binds a greater fraction of moisture even at higher temperatures, leading to suppressed dielectric activity. Consequently, the influence of secondary bonding interactions was investigated to understand the impact of temperature on the absorbed water molecules in a composite epoxy matrix.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...