How a water drop removes a particle from a hydrophobic surface†
Abstract
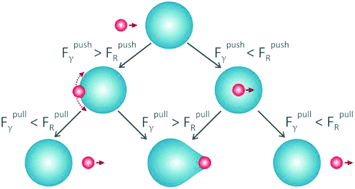
To understand the removal of particles from surfaces by water drops, we used an inverted laser scanning confocal microscope to image the collision between a water drop and a particle on a flat polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) surface. The dynamic drop–particle contact line was monitored by fixing the drop directly above the objective lens while moving the sample stage at well-defined speeds (10–500 μm s−1). The lateral force acting on the drop during the collision was measured as a function of speed, using a force sensor mounted on the microscope. Depending on the collision speed, the particle either stays attached at the rear of the drop or detaches from it. We propose a criterion to determine whether the particle remains attached to the drop based on the capillary and resistive forces acting on the particle during the collision. The forces measured when the particle crosses the air–water interface are compared to existing models. We adapted these to account for rolling of the particle. By comparing our experimental measurements with an analytical model for the capillary torque acting on a particle rolling at an interface, we provide detailed insights on the origins of the resistive force acting on the particle when it is pushed or pulled by the drop. A low friction force between the surface and the particle increases the likelihood of particle removal.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...