Non-equilibrium growth and twist of cross-linked collagen fibrils
Abstract
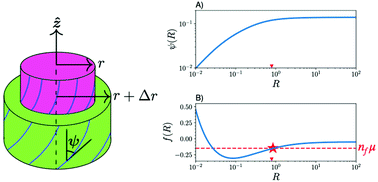
The lysyl oxidase (LOX) enzyme that catalyses cross-link formation during the assembly of collagen fibrils in vivo is too large to diffuse within assembled fibrils, and so is incompatible with a fully equilibrium mechanism for fibril formation. We propose that enzymatic cross-links are formed at the fibril surface during the growth of collagen fibrils; as a consequence no significant reorientation of previously cross-linked collagen molecules occurs inside collagen fibrils during fibril growth in vivo. By imposing local equilibrium only at the fibril surface, we develop a coarse-grained quantitative model of in vivo fibril structure that incorporates a double-twist orientation of collagen molecules and a periodic D-band density modulation along the fibril axis. Radial growth is controlled by the concentration of available collagen molecules outside the fibril. In contrast with earlier equilibrium models of fibril structure, we find that all fibrils can exhibit a core–shell structure that is controlled only by the fibril radius. At small radii a core is developed with a linear double-twist structure as a function of radius. Within the core the double-twist structure is largely independent of the D-band. Within the shell at larger radii, the structure approaches a constant twist configuration that is strongly coupled with the D-band. We suggest a stable radius control mechanism that corneal fibrils can exploit near the edge of the linear core regime; while larger tendon fibrils use a cruder version of growth control that does not select a preferred radius.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...