Fundamental understanding of electrochemical catalytic performance of carbonized natural wood: wood species and carbonization temperature†
Abstract
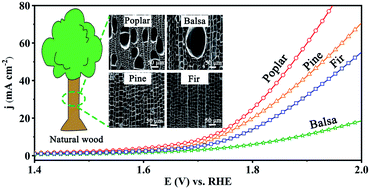
Natural wood has attracted enormous attention in the electrocatalysis field due to its hierarchical porous structure and excellent electrical conductivity after carbonization. Different wood species as a carbon substrate have a significant impact on the electrocatalytic performance. Herein, to fundamentally understand the electrochemical catalytic performance of carbonized natural wood, the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) performances of various carbonized wood (pine, fir, poplar, and balsa) calcined at different temperature were studied. The OER performance of wood carbon was improved with the increase of carbonization temperature, and better OER performance was obtained at a carbonization temperature of 900 °C. The overpotentials of pine carbon, fir carbon, poplar carbon, and balsa carbon are 507 mV, 539 mV, 490 mV, and 651 mV, respectively, at a current density of 10 mA cm−2. The pore structure of wood carbon significantly affected the OER activity. Among the four types of wood carbon, poplar carbon exhibited better electrocatalytic activity due to its cross-distribution of pores and pore diameter. This work is conducive to the selection of suitable wood carbon substrates for the preparation of environmentally friendly electrocatalysts, and is of great significance for improving the efficiency of electrocatalytic water splitting to produce clean and sustainable hydrogen energy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...