A gallic acid based metal organic framework derived NiS/C anode for sodium ion batteries†
Abstract
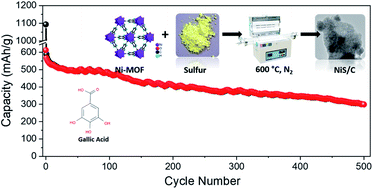
Strategies have been tailored to enhance electro-active material capacities and the cycle lives of sodium-ion batteries. Amongst the available electrode materials, metal–organic framework derived anode materials have begun to stand out because of their versatile compositions, structures, and textures, leading to high specific surface areas and more active electrochemical reaction sites. Herein, Ni-MOF is first prepared from a bio-available organic linker, namely gallic acid, in a benign solvent (water). Then a nickel sulfide/carbon (NiS/C) composite is synthesized via concurrent sulfuration and carbonization under nitrogen flow at 600 °C. Carbon-encapsulated NiS particles are formed, in which the carbon framework both prevents the volume expansion of NiS during discharge and also gives rise to higher conductivity. The resulting NiS/C composite is tested as a potential anode material for sodium-ion batteries and it delivered a capacity of around 208 mA h g−1 at a current density of 1475 mA g−1 after 500 charge/discharge cycles. The Na+-ion diffusion rate is calculated through Warburg impedance analysis, and values of 1.8 × 10−16 and 3.5 × 10−15 S cm−1 are obtained initially and after cell operations are terminated, respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...