Enhanced solar cell performance of Cu2ZnSnSe4 thin films through structural control by using selenide stacked nanolayers in a non-toxic selenium atmosphere
Abstract
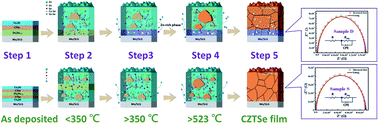
A double layer distribution can be observed in Cu2SnZnSe4 (CZTSe) thin films prepared via the selenization of metallic precursors. The double layer structure may cause the back contact of Mo substrates with absorber layers to degrade, thereby suppressing the performance of solar cells. Hence, to eliminate the problematic structure, we reduced the loss of SnSex during the selenization of precursors by modifying the laminated structures of the precursors formed by the deposition of CuxSe and ZnxSn1−x. In addition, the effects of different laminated structures on the thin-film properties of CZTSe were studied through X-ray diffraction analysis, field emission scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectroscopy, secondary-ion mass spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy. The results demonstrate that the changes in the laminated structures help in reducing the loss of SnSex and in promoting the reactions between ZnSe and Cu–Sn–Se. As a result, the drawbacks of CZTSe thin films, such as the double layer distribution and existence of air holes, can be addressed. Furthermore, changes in the crystal structures are also noted. Photoluminescence results reveal that signals indicative of ZnSe-related defects were weakened and the band-tail effects became insignificant. Moreover, the internal resistance and quality of the interface in CZTSe solar cells were investigated through electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The results prove that the improvement of the double-layer distribution of absorber layers leads to high photoelectric conversion efficiency. Therefore, we modified the laminated structures of precursors to eliminate the distribution of absorber layers, which considerably improved the photoelectric conversion efficiency (from 2.9% to 5.67%).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...