Degradation mechanisms of lithium sulfide (Li2S) composite cathode in carbonate electrolyte and improvement by increasing electrolyte concentration†
Abstract
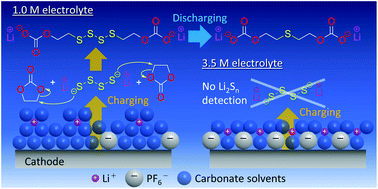
A Li2S cathode has a high theoretical capacity (1166 mA h g−1); however, it is inherently an insulator. To remedy this defect, composite sulfides can be prepared with transition-metal sulfides having better conductivity than Li2S. Among them, a Li8FeS5 (Li2S/FeS = 4/1, mol/mol) cathode theoretically delivers 888 mA h g−1. This cathode, however, exhibits poor cycling performance in 1.0 M LiPF6/ethylene carbonate (EC)–dimethyl carbonate (DMC) (EC/DMC = 1/1, v/v) electrolyte; meanwhile, concentrated (3.5 M) electrolyte improves the performance. Herein, we elucidate the degradation mechanisms through analyses of cycled electrolytes and cathode surfaces. We identify organic polysulfides (R–Sn–R) (not lithium polysulfides (Li2Sn)) after charging and organic sulfides (R–S–R) after discharging in the 1.0 M electrolyte. Meanwhile, neither are detected in the 3.5 M electrolyte; instead, salt decomposition products (mainly LiF) are detected on the cathode surface. Therefore, electrolyte modifications can further improve the cyclability of sulfur-based secondary batteries including lithium–sulfur battery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...