Modulation of the electronic structure and thermoelectric properties of orthorhombic and cubic SnSe by AgBiSe2 alloying†
Abstract
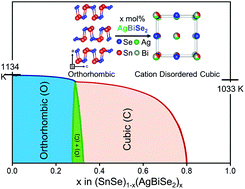
Recently, single-crystals of tin selenide (SnSe) have drawn immense attention in the field of thermoelectrics due to their anisotropic layered crystal structure and ultra-low lattice thermal conductivity. Layered SnSe has an orthorhombic crystal structure (Pnma) at ambient conditions. However, the cubic rock-salt phase (Fm![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m) of SnSe can only be stabilized at very high pressure and thus, the experimental realization of the cubic phase remains elusive. Herein, we have successfully stabilized the high-pressure cubic rock-salt phase of SnSe by alloying with AgBiSe2 (0.30 ≤ x ≤ 0.80) at ambient temperature and pressure. The orthorhombic polycrystalline phase is stable in (SnSe)1−x(AgBiSe2)x in the composition range of 0.00 ≤ x < 0.28, which corresponds to narrow band gap semiconductors, whereas the band gap closes upon increasing the concentration of AgBiSe2 (0.30 ≤ x < 0.70) leading to the cubic rock-salt structure. We confirmed the stabilization of the cubic structure at x = 0.30 and associated changes in the electronic structure using first-principles theoretical calculations. The pristine cubic SnSe exhibited the topological crystalline insulator (TCI) quantum phase, but the cubic (SnSe)1−x(AgBiSe2)x (x = 0.33) showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with overlapping conduction and valence bands. The cubic polycrystalline (SnSe)1−x(AgBiSe2)x (x = 0.30) sample showed n-type conduction at room temperature, while the orthorhombic (SnSe)1−x(AgBiSe2)x (0.00 ≤ x < 0.28) samples retained p-type character. Thus, by optimizing the electronic structure and the thermoelectric properties of polycrystalline SnSe, a high zT of 1.3 at 823 K has been achieved in (SnSe)0.78(AgBiSe2)0.22.
m) of SnSe can only be stabilized at very high pressure and thus, the experimental realization of the cubic phase remains elusive. Herein, we have successfully stabilized the high-pressure cubic rock-salt phase of SnSe by alloying with AgBiSe2 (0.30 ≤ x ≤ 0.80) at ambient temperature and pressure. The orthorhombic polycrystalline phase is stable in (SnSe)1−x(AgBiSe2)x in the composition range of 0.00 ≤ x < 0.28, which corresponds to narrow band gap semiconductors, whereas the band gap closes upon increasing the concentration of AgBiSe2 (0.30 ≤ x < 0.70) leading to the cubic rock-salt structure. We confirmed the stabilization of the cubic structure at x = 0.30 and associated changes in the electronic structure using first-principles theoretical calculations. The pristine cubic SnSe exhibited the topological crystalline insulator (TCI) quantum phase, but the cubic (SnSe)1−x(AgBiSe2)x (x = 0.33) showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with overlapping conduction and valence bands. The cubic polycrystalline (SnSe)1−x(AgBiSe2)x (x = 0.30) sample showed n-type conduction at room temperature, while the orthorhombic (SnSe)1−x(AgBiSe2)x (0.00 ≤ x < 0.28) samples retained p-type character. Thus, by optimizing the electronic structure and the thermoelectric properties of polycrystalline SnSe, a high zT of 1.3 at 823 K has been achieved in (SnSe)0.78(AgBiSe2)0.22.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...