Whole-cell screening of oxidative enzymes using genetically encoded sensors†
Abstract
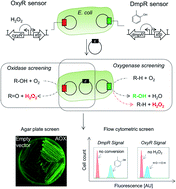
Biocatalysis is increasingly used for synthetic purposes in the chemical and especially the pharmaceutical industry. Enzyme discovery and optimization which is frequently needed to improve biocatalytic performance rely on high-throughput methods for activity determination. These methods should ideally be generic and applicable to entire enzyme families. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a product of several biocatalytic oxidations and its formation can serve as a proxy for oxidative activity. We designed a genetically encoded sensor for activity measurement of oxidative biocatalysts via the amount of intracellularly-formed H2O2. A key component of the sensor is an H2O2-sensitive transcriptional regulator, OxyR, which is used to control the expression levels of fluorescent proteins. We employed the OxyR sensor to monitor the oxidation of glycerol to glyceraldehyde and of toluene to o-cresol catalysed by recombinant E. coli expressing an alcohol oxidase and a P450 monooxygenase, respectively. In case of the P450 BM3-catalysed reaction, we additionally monitored o-cresol formation via a second genetically encoded sensor based on the phenol-sensitive transcriptional activator, DmpR, and an orthogonal fluorescent reporter protein. Single round screens of mutant libraries by flow cytometry or by visual inspection of colonies on agar plates yielded significantly improved oxidase and oxygenase variants thus exemplifying the suitability of the sensor system to accurately assess whole-cell oxidations in a high-throughput manner.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...